What is a Wet Signature?
A wet signature is a traditional, handwritten mark made with ink, often required for legal and formal documents. This form of signature is considered the traditional method for authenticating agreements and documents.
When is a wet signature required?
Despite a significant shift towards electronic signatures for many types of documents, a wet signature can still be required in many situations where handwritten authentication is necessary to verify identity, intent or prevent fraud. The physical presence of a handwritten mark is seen as a clear indication of the signer’s intent to agree to the terms within the document.
Documents that typically need a wet signature include:
- Wills and trusts
- Loan agreements
- Certain property documents
- Court orders and legal filings
- Notarised documents
- Government applications
Wet signatures vs electronic signatures: The key differences
As businesses and individuals move toward digital processes, the differences between wet signatures and electronic signatures become more important. While both serve the same purpose—authenticating documents and agreements—they differ significantly in terms of security, legality, convenience, and cost.
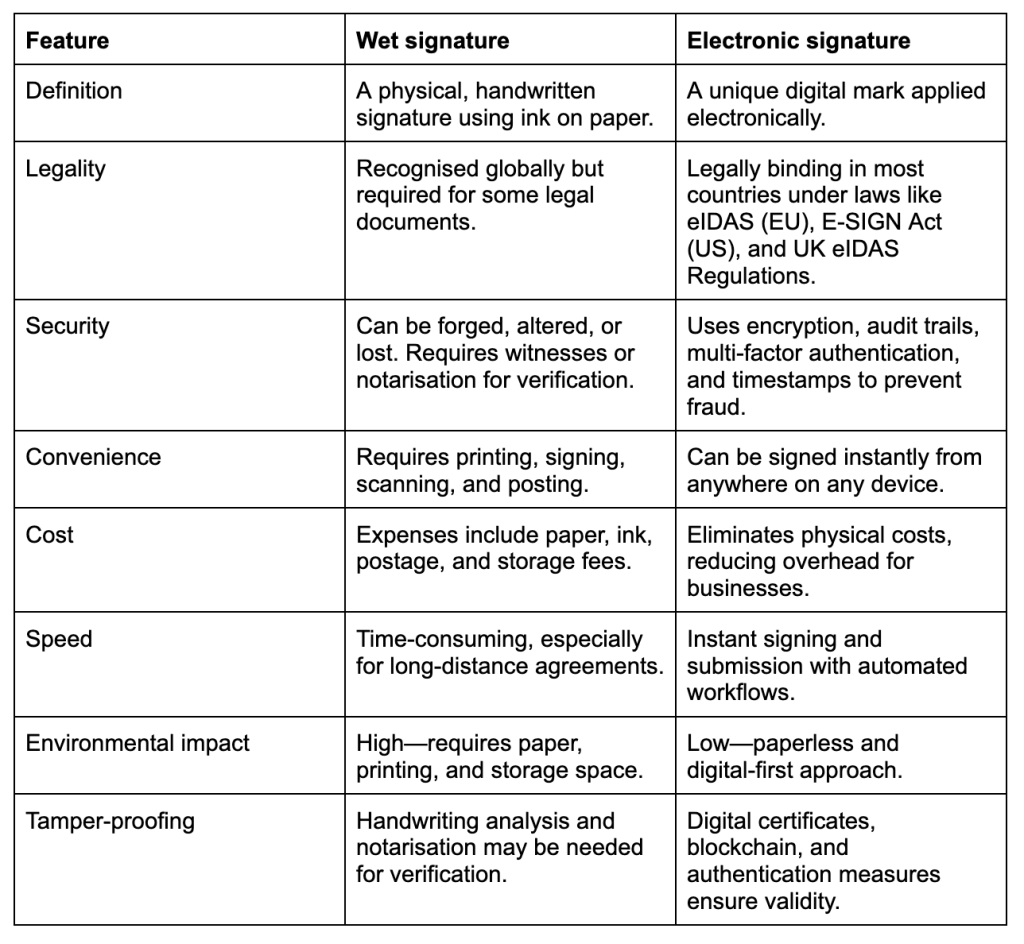
Are e-signatures as secure as wet signatures?
Yes, electronic signatures are more secure than traditional wet signatures. This is because they typically involve the use of a secure, encrypted platform to sign a document. These signatures come with advanced security features that make them more resilient to fraud than wet signatures:
Encryption
eSignatures are encrypted, which means they are virtually tamper-proof. Once a document is signed, any alteration would invalidate the signature.
Authentication
High-quality e-signature platforms like E-Sign require multi-factor authentication (MFA), such as email or SMS pin protection, adding an additional layer of security.
Audit trails
eSignature services create detailed audit trails that log who signed, when, and where, which cannot be easily altered or deleted. This provides a permanent record of the signing process.
Blockchain technology
Blockchain technology offers an even higher level of security by making signed documents tamper-proof and publicly verifiable.
Security and fraud concerns with wet signatures
While wet signatures have been a trusted form of authentication for many years, they come with security risks that make them vulnerable to forgery, tampering, and loss. Unlike electronic signatures, which use encryption and audit trails, wet signatures rely on physical verification methods that can be easier to manipulate.
Common security risks of wet signatures
- Forgery – when someone copies or fakes a handwritten signature.
- Alteration – a signed document is modified after signing (e.g., contract terms changed).
- Loss or theft – physical documents can be stolen, misplaced, or destroyed.
- Lack of verification – no digital authentication, making it hard to prove identity.
Are electronic signatures legally binding?
In many cases, yes, electronic signatures are legally binding, with the most secure and robust type of e-signature (qualified) having the same legal weight and validity as a wet signature.
To find out more about the legalities of e-signatures, check out our guide: The Legalities of eSignatures in 2025