How to Use eSignatures with HIPAA Documents
PUBLISHED
21st August, 2024
Contents
HIPAA is the cornerstone of safeguarding patient privacy, ensuring healthcare organisations and their partners uphold top-tier security standards to protect sensitive patient information. Data privacy is a complex issue, as technological advancements over the years have resulted not only in the system improvements that keep patient information secure. But also the cyber threats that the data needs to be safeguarded from. For this reason, it’s essential that healthcare organisations understand what HIPAA is and the steps they need to take in order to maintain compliance with it.
What is HIPAA?
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was initially established in 1996 to empower healthcare patients with greater authority over their protected health information (PHI). Following several revisions, the legislation was officially enacted in the United States in 2003. HIPAA encompasses a series of regulations and guidelines designed to safeguard the privacy and security of patient data.
When HIPAA was implemented, it set a general standard for how covered entities like medical clinics, doctors, insurance companies, and more should handle PHI when it is electronically transferred and stored. HIPAA has two established directives as part of the regulation; the Privacy Rule and the Security Rule.
- Privacy Rule – defines the standards for PHI which includes information like demographic data, lab results, and medical history.
- Security Rule – outlines national standards to protect an individual’s electronic health information that a covered entity has created, collected, used, or maintained. This rule requires sufficient safeguards to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and security of PHI.
What information does HIPAA cover?
The HIPAA regulation is highly detailed, with extensive information provided for organisations in order to effectively protect patient data. It covers the following:
- Information that relates to the healthcare services provided to an individual, including insurance and payment details.
- Personal identifying information that is gathered, used, or disclosed during healthcare processes. For example names, addresses, or social security numbers.
- Details regarding a person’s medical history or their present or future physical and mental health.
It’s important to note that HIPAA applies to all types of protected health information, whether it is electronic, oral, or written. Also, it covers a wide range of different healthcare organisations as well as business associates they collaborate with.
Can Electronic Signatures be used Under HIPAA Rules?
Electronic signatures can be used on HIPAA documents, however there are no specific guidelines for how they should be used to maintain compliance. It is therefore the responsibility of the covered entity to ensure that any e-signature applied to a digital document, results in a legally binding contract.
This is according to the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) who also state “the Privacy Rule generally allows for electronic documents, including business associate contracts, to qualify as written documents for purposes of meeting the Rule’s requirements.”
Overall this means that as long as it conforms to state law in terms of legality and security, e-signatures and e-signature solutions can be used to sign documents. As they maintain the integrity of PHI and don’t violate the rules of HIPAA in any way.
What is a Business Associate and Business Associate Agreement (BAA)?
A business associate is a third-party entity that partners with a covered entity to provide services that require access to or disclosure of protected health information (PHI). To safeguard this information, Business Associate Agreements are established between the covered entity and the business associate. These contracts mandate that both parties adopt appropriate measures to ensure the privacy, integrity, and security of patient health data.
The agreement will outline what is and is not allowed between the parties in addition to their responsibilities for safeguarding PHI. In specific circumstances BAAs must be in place between a covered entity and a business associate. Examples of covered entities that must sign agreements with associates include:
- Clinics
- Dentists
- Doctors
- Nursing homes
- HMOs
- Pharmacies
- Health insurance companies
How to ensure your e-signatures are HIPAA compliant
Electronic signatures and digital solutions are a useful way for healthcare organisations and professionals to validate forms, and ensure they are protected from violations of the HIPAA rules. In order to guarantee that the e-signatures used in your organisation are compliant with HIPAA, you need to confirm their legality by adhering to the criteria set out in the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (ESIGN Act) and the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA).
Both Acts affirm that electronic signatures and digital records hold the same legal weight as handwritten signatures on paper documents. The ESIGN Act authorises the use of electronic signatures in the US across all 50 states when federal law is applicable.
It states that “a document or signature cannot be denied legal effect or enforceability solely because it is in electronic form.” These Acts enable highly secure methods for signer authentication, significantly reducing the risk of tampering and therefore preserving document integrity. Consequently, secure electronic signature solutions are deemed valid and legally binding.
What is considered to be a violation of HIPAA?
As well as knowing how to be compliant with HIPAA, it can be beneficial to understand what is classed as a violation of the act too. Especially as they can result in a substantial penalty. The HIPAA Journal states that the most common violations are due to:
- Improper disclosure of PHI
- Failing to complete a risk analysis
- Failing to encrypt electronic health information
- Delayed notification of a breach when one occurs
- Failing to obtain a HIPAA compliant Business Associate Agreement
How can e-signatures improve your compliance with HIPAA?
E-Signatures can help to improve compliance with HIPAA because they simplify the process for gathering consent and approval from patients in relation to treatments and how their PHI is used. Whilst maintaining suitable storage and tracking of the data. Therefore, by using a highly secure and user-friendly digital solution like eSign, healthcare providers and organisations can improve patient care, as well as reducing the risk of expensive violations of HIPAA.
How is eSign HIPAA compliant?
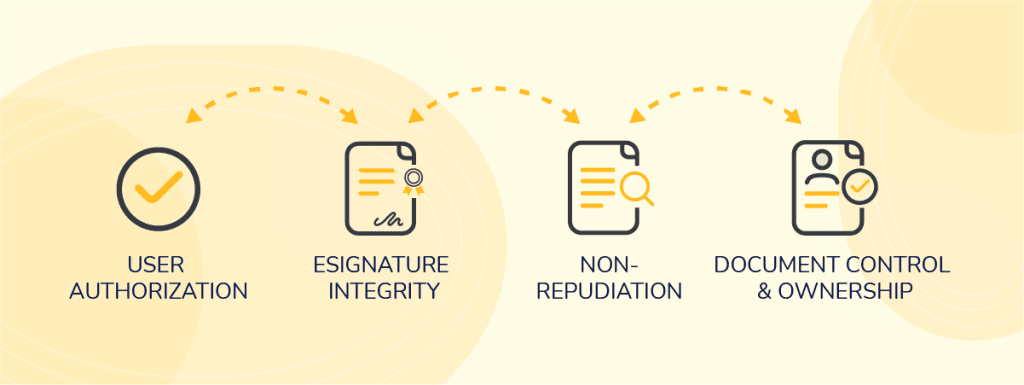
The eSign platform has various features and processes in place that effectively protect user data, making it a fully HIPAA compliant solution. Read on to see how eSign complies with HIPAA below.
User authorisation
An important part of HIPAA compliance and one of the biggest challenges in ensuring electronic signatures are legally binding, is the ability to validate the identity of individuals signing documents. When sending documents to patients, you are required to check that all disclosures are made in accordance with the HIPAA Privacy and Security Rules. Therefore, your documents need to be validated and secured to avoid breaching patient privacy. eSign has multiple methods of authorisation to support HIPAA compliance including two-factor and SMS authentication.
eSignature integrity
The main priority for healthcare organisations in maintaining HIPAA compliance with the Security Rule is keeping PHI secure. Which is why they need systems implemented that will prevent digital tampering of documents and e-signatures. This can be achieved through eSign by controlling access to stored documents with robust password protection.
Non-repudiation
A clear and detailed audit trail for electronic signatures is essential in ensuring that any individual or party that signs a document cannot deny that they have done so. Every document signed through eSign comes with an accurate audit trail including key details like the date, time, location, and IP address of the e-signature.
An audit trail confirms the legality of the e-signature, meaning parties cannot later argue authorisation for sharing PHI. With eSign you will be notified when a signer has completed their part of the document. Allowing you to optimise the process from beginning to end. Also, each signer will be provided with a copy of the signed document, to avoid non-repudiation issues.
Document control and ownership
In order to protect the integrity and prove authenticity of signed documents, covered entities must have control and ownership over the e-signature and evidence of it. eSign can provide this in the form of a digital certificate. Which certifies the authenticity of the signed document. Secure storage and accessibility to documents is also important. As you will need to have an effective way to find the files you need when you need them.
Conclusion
By confirming that your processes and systems are HIPAA compliant, you can avoid a costly penalty and improve patient care within your organisation. eSign’s industry leading e-signature and digital document solution meets all requirements for HIPAA and legal regulations for the use of electronic signatures, making it the ideal secure platform for healthcare organisations and providers.
To find out more about our HIPAA compliance or how eSign can benefit your organisation, get in touch with our digital transformation team who will be happy to discuss with you. You can also try the platform for yourself by registering for our 14-day free trial, allowing you to gain a better insight into the features and functionality, before choosing a plan that suits your document requirements.
 Facebook
Facebook
 X (Twitter)
X (Twitter)
 LinkedIn
LinkedIn











