What is an eSignature: The Complete Guide
Laura Cain
Marketing & Brand Manager
PUBLISHED
13th November, 2024
If your business is looking to streamline its document processes, save time, increase efficiency, and become more sustainable, implementing an e-signature solution is the ideal way to achieve all of these goals and more. But what exactly is an eSignature?
In this guide, we’ll be explaining everything you need to know about electronic signatures, including what they are, their legal validity, the benefits of using them, choosing the right platform, and practical tips for implementing them into your processes. By having a more in-depth understanding of e-signatures, you will be able to more effectively incorporate them into your document workflows and maximise the benefits of switching from paper to digital.
What is an electronic signature?
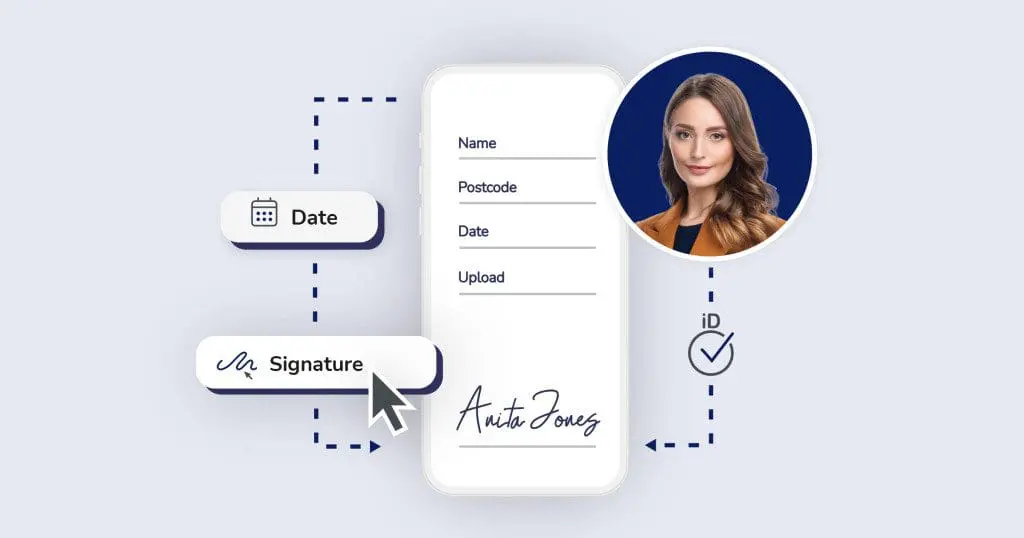
An electronic signature or e-signature is the use of a digital element, impression, or markup to confirm that the individual signing a document agrees to the contents written within it. It acts as a digital alternative to handwritten signatures which are added to paper documents. Before eSignatures, it was a time-consuming and frustrating process when needing to sign an online document. You would need to print out the document, sign it by hand, and scan it back in to create a digital copy.
Technology has advanced significantly in recent years and with that has come the ability to digitally sign documents in a much more convenient and secure way than before. eSignatures provide a fast and efficient way to sign documents and streamline business processes across many industries, with the added benefit of reducing paper usage. Less paper means fewer trees need to be cut down, which works to reduce carbon emissions and the negative impact on the planet.
What are the different types of e-signature?

There are three main types of electronic signatures which are defined in the ‘electronic identification and trust services’ (eIDAS) regulation. Each type of eSignature under the regulation offers an increased level of security and assurance.
Simple eSignatures
Simple eSignatures (SES) are the most basic and easiest to implement as there is no identity verification required. A signature can be added to a document by anyone who opens it whether that is by drawing the signature, typing it, uploading an image, or ticking a checkbox.
This makes them an ideal option for instances where a basic document needs to be signed, that won’t have a significant legal implication. Simple signatures are legally binding in some cases, but there are industries and scenarios that require a higher level of authenticity in order for the signature to be legally accepted.
Due to the lack of verification, similar to a traditional wet signature, simple eSignatures can be easier to forge, which is why they are best utilised on non-official documents.
Advanced eSignatures
Advanced electronic signatures (AES) are linked to specific signers with an “electronic seal” attached to them. This allows the signer to be formally identified as they are sent using an electronic registered delivery service (ERDS) for further verification.
By transmitting them this way, audit trails and other forms of evidence surrounding the data being transmitted can be provided. Advanced eSignatures are often issued with a unique digital signature certificate.
In accordance with eIDAS, advanced electronic signatures must meet the following criteria in order to qualify:
- Correctly identify the signer
- Be specifically linked to the signer and only them
- Have been created using eSignature data that the signer has full control over and confidence that they have the sole ability to sign it
- Connected to data in a document that the signer(s) can monitor for any further changes
In order to meet the criteria, AES uses a technology known as Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), which is essentially how a digital certificate verifies an electronic signature. A digital certificate is similar to other official documents like a passport or driving licence as it has been verified by an official third party. Also, the certificate is highly secure as it is unique to the relevant individual and would be practically impossible to replicate.
Qualified eSignatures
Qualified electronic signatures (QES) are similar to advanced signatures, however, they go a step further to meet additional requirements set out by the eIDAS regulations. They must be certified based on public keys that have been issued using proper technological means. This means that the identity verification process is multi-step, using both encrypted keys and two-factor authentication.
Essentially, a third party that has been previously agreed upon will vet the signers before they can provide a QES. Third-party identification of the signer can be completed face-to-face remotely via an online video chat or in person. It’s important to note that only an eSignature provider that is accredited as a Qualified Trust Service Provider (QTSP) can issue qualified certificates.
Both types of eSignatures meet the highest industry standards, as they each provide every user with their own unique key that is directly linked to the signer’s identity. You can have complete peace of mind that the signature is valid and secure when using either an AES or QES.
The eIDAS regulation requirements for qualified electronic signatures include:
- Ensure only one use of the signature is allowed
- Protect the confidentiality of the signature creation data
- Be suitably protected by the legitimate signer
- Shield the signature from forgery
- Not change the data in any way or stop it from being presented to the signer before their signature
- Create or manage data on behalf of the signer only when requested by the qualified trust provider
Legal validity and compliance
One of the main questions asked about electronic signatures is are they legally binding? And the answer is yes. eSignatures are legally valid and binding, with several countries now having regulations in place to support their use. We’ll be exploring some of these regulations in more detail below.
UK and EU law
Electronic signatures have been legally binding in the UK since 2000 when the Electronic Communication Act was introduced. They have also been part of European law since 2016 through the eIDAS regulation. The eIDAS regulation established the framework to ensure that electronic interactions between businesses are safer and more efficient. The regulation applies to both the UK and Europe but was amended for the UK in 2018 when it withdrew from the European Union.
The purpose of eIDAS is to enforce the specific requirements providers must follow in order to gain a qualified status and increase confidence for users who are considering using electronic signatures. However, even with this regulation in place, there was still uncertainty surrounding the use of eSignatures. Much of this uncertainty was resolved in 2019 when the Law Commission confirmed the validity and legality of electronic signatures in executing documents, including documents where there is a statutory requirement for a signature.
United States law
In the United States, there are three main laws that cover the use of eSignatures: the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce (ESIGN) Act, the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA), and the Digital Signature and Electronic Authentication Law. The ESIGN Act is the predominant regulation for eSignatures, allowing their use in all 50 states when federal law applies.
Under the Act, an e-signature is defined as an electronic sound, symbol, or process that is attached to or associated with a document, and executed or adopted by an individual with the intent to sign and be legally bound by the signature.
Legal requirements for e-signatures
The exact e-signature legal requirements can vary from country to country, but there are some common requirements to be aware of when considering the overall legality of electronic signatures.
- Identification – the signature must be uniquely linked to the signer and only them, with the ability to identify them.
- Data link – the signature must be linked to the data it relates to, this will ensure that any changes to the data can be identified.
- Control – the signer must have full control over the signature and the means used to create it.
- Protecting the signature – the signature must be securely attached to the document and not stored separately. Proper security measures will prevent tampering with the signature.
- Copy to signer – a copy of the signed document must be provided to the signer once finalised.
Benefits of using electronic signatures
There are several benefits of switching to eSignatures for your document processes, including:
- Reduce paper use – moving away from paper-based processes will help your business become much more efficient. Going paperless can also contribute to your sustainability goals as you won’t have to waste paper by printing, hand signing, and scanning documents back in.
- Save time – using electronic signatures can significantly reduce your document turnaround times, thanks to the convenience of signing within a few minutes rather than potentially hours or days depending on their access to a printer etc. As a result, you can complete documents and close deals much faster.
- Cut unnecessary costs – paper and accessories related to paper processes such as printers, files, fax machines etc, are expensive. But by digitising your document transactions you can reduce or even eliminate the spending associated with paper, freeing up extra budget that can be allocated to other key parts of your business.
- Increase productivity – by removing slow and inefficient paper-based transactions, you can boost productivity within your business through streamlined processes that are quicker and easier for your team to follow.
- Automate operations – with E-Sign, you have the ability to integrate our platform with existing applications you already use, making it simple to create automated workflows and ensure your systems operate seamlessly with each other.
- Upgrade the user experience – keeping everything digital ultimately makes life easier for your clients, allowing them to view, e-sign and return your company documents simply by clicking on an email.
- Enhance security – when you opt for a secure e-signature and document management platform like E-Sign, you can be sure that your business is benefitting from increased security. We ensure that your information is protected by commercial-grade firewalls, border routers, network management systems and encryption.
Choosing the right e-signature tool or platform

Deciding to acquire an electronic signature is just the first step of your digital journey, you then need to find the right tool or platform that will meet your business needs and document requirements. Below are some essential factors to consider when researching providers and selecting a digital signature service.
Avoid prioritising price
Before we delve into the factors to consider when choosing an e-signature provider, it’s important to address the potential drawbacks of selecting a digital solution based solely on price. The market is flooded with various e-signature software options, each with its own pricing structure.
While it might be tempting to choose the cheapest option, it’s crucial to remember that an electronic signature needs to be both legally binding and secure, especially for handling sensitive documents. A lower-cost solution might not provide the quality and reliability you need.
Focusing only on price can lead to additional costs in the long run, either by upgrading to a higher-quality service or by investing more time and resources into finding a provider that meets your requirements from the start.
Compliance and security
When signing important digital documents, signers need to feel assured that their data is completely secure. Consequently, any eSignature providers you consider should demonstrate that they meet or exceed the necessary industry standards for security and comply with relevant regulations in their operational areas.
E-Sign’s services are compliant with all relevant UK regulations and standards, including GDPR, which we continually monitor for updates to the regulatory guidance and interpretations of key GDPR requirements to maintain our ongoing compliance. Security and privacy are at the core of our values at E-Sign. We have implemented the highest standard of systems, protocols, and policies to ensure our user data is kept as secure as possible.
Integrations and automation
Many organisations utilise a variety of digital systems and applications to manage their processes and workflows. When evaluating different e-signature providers, it’s essential to consider whether they offer integrations with other platforms to streamline your operations and enhance efficiency.
Seamless integrations can save you the hassle of switching between applications to complete important transactions effectively. A reliable, high-quality e-signature platform should integrate smoothly with your existing systems, providing a comprehensive view of your business pipeline and reducing administrative tasks.
Practical steps for implementing e-signatures
The best place to start when implementing e-signatures into your processes is to establish the use cases for the platform and the features needed to meet your business requirements. A good approach for this is to work with relevant stakeholders from different parts of your organisation and determine the simplest use cases initially that will have the biggest impact.
Consider key parameters like implementation speed and the impact on ROI during the evaluation. By finding quick wins with the software you demonstrate its value to senior management.
Assessing use cases is just the first step in the process of implementing and expanding your e-signature solution. The other steps include:
- Approach new business groups – understand their current signing processes, any pain points or issues in their workflows, and highlight how e-signature technology can benefit them.
- Qualification checklist – carry out a more in-depth analysis of the specific requirements for each use case.
- Demonstration – use case-specific demonstrations with key stakeholders to promote the solution internally.
- Deployment plan – keep the project on track with milestones and deliverables clearly presented to stakeholders along with a timeline to go live.
- Internal marketing – highlight the reasons behind the new solution for staff and keep them updated, engaged, and informed, throughout the implementation process with pre and post-launch internal communications.
How to create an electronic signature
You can easily generate a secure and legally binding electronic signature with E-Sign. Once you have created an account, simply log in and click on the ‘My Signature’ tab in the lefthand column of your dashboard. From there you will be presented with three different options for creating your online signature.
These options are typing your signature into the box shown, drawing it using a mouse or your finger using a touchscreen device, or uploading it in the box shown (your signature can be uploaded as a JPEG or PNG file). Once you have finalised your signature, it is transformed into a ready-made e-signature that is just as distinctive and unique to your identity as its handwritten counterpart. The signature can then be affixed to any important documents going forward, in a highly secure and legally recognised way.
Conclusion
We hope this guide has helped you gain a better understanding of eSignatures and the most important details you want to know about them. This should provide you with everything you need to find and implement a secure and legally binding electronic signature system that meets your business requirements.
E-Sign is an industry-leading provider of secure eSignature and digital document solutions, offering customised services to meet a variety of business needs. If you’re looking to digitise your document processes and reap the benefits of electronic signatures, consider trying E-Sign. We offer a 14-day free trial, allowing you to explore the platform’s features and see how it can support your document requirements.
If you have any questions or queries, please don’t hesitate to contact us, our digital transformation specialists are on hand to help.
 Facebook
Facebook
 X (Twitter)
X (Twitter)
 LinkedIn
LinkedIn











